Topic: Application of bioinformatics analysis in brain diseases.
Speaker 1 : Jiaqi Hao, M.Med. Candidate
Date: 17/06/2024, 14:00
Location: The lab of HMRRC (10011, the 8th Teaching Building)
Speaker 1: Jiaqi Hao, M.Med. Candidate
Keypoints:
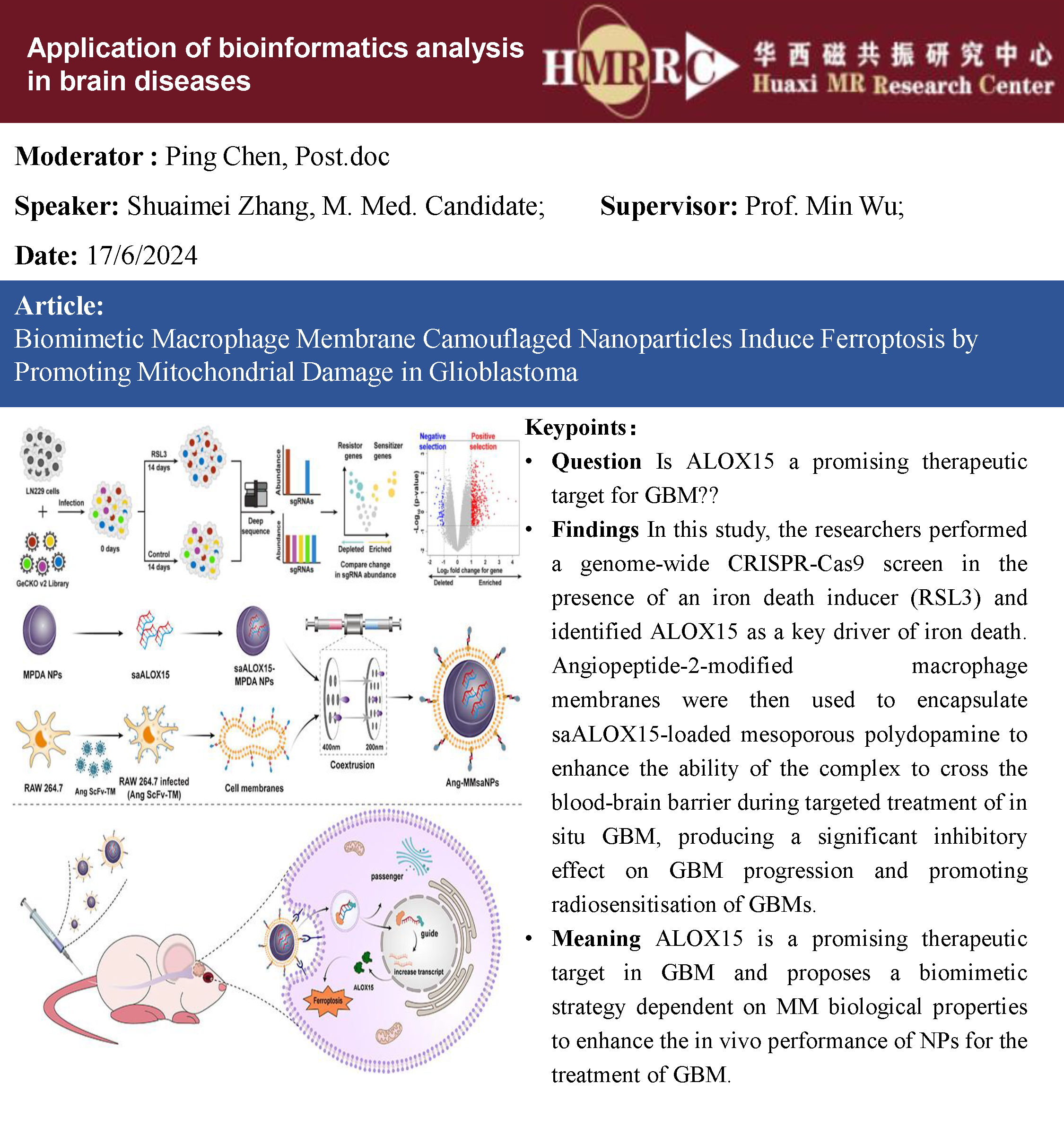
Question: Is DNALI1 a promising thera-peutic target for TBI?
Findings: The article identifies a crucial protein, axonemal dynein light intermediate polypeptide 1 (DNALI1), and elucidated its potential pathogenic role in post-TBI neurodegeneration. The DNALI1 gene is systematically screened through analyses of Aging, Dementia, and TBI studies, con-firming its elevated expression both in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, it is observed that altered DNALI1 expression under normal conditions has no discernible effect. However, upon overexpression, DNALI1 inhibits autophagosome-lysosome fusion, reduces autophagic flux, and exacerbates cell death under pathological conditions. DNALI1 silencing significantly enhances autophagic flux and alleviates neurode-generation in a CTE model.
Meaning: Traumatic brain injury (TBI) leads to progressive neurodegeneration that may be caused by chronic traumatic encepha-lopathy (CTE).These findings highlight DNALI1 as a potential key target for pre-venting TBI-related neurodegeneration.
Speaker 2: Shuaimei Zhang, M. Med. Candidate
Title: Biomimetic Macrophage Membrane Camouflaged Nanoparticles Induce Ferroptosis by Promoting Mitochondrial Damage in Glioblastoma.
Keypoints:
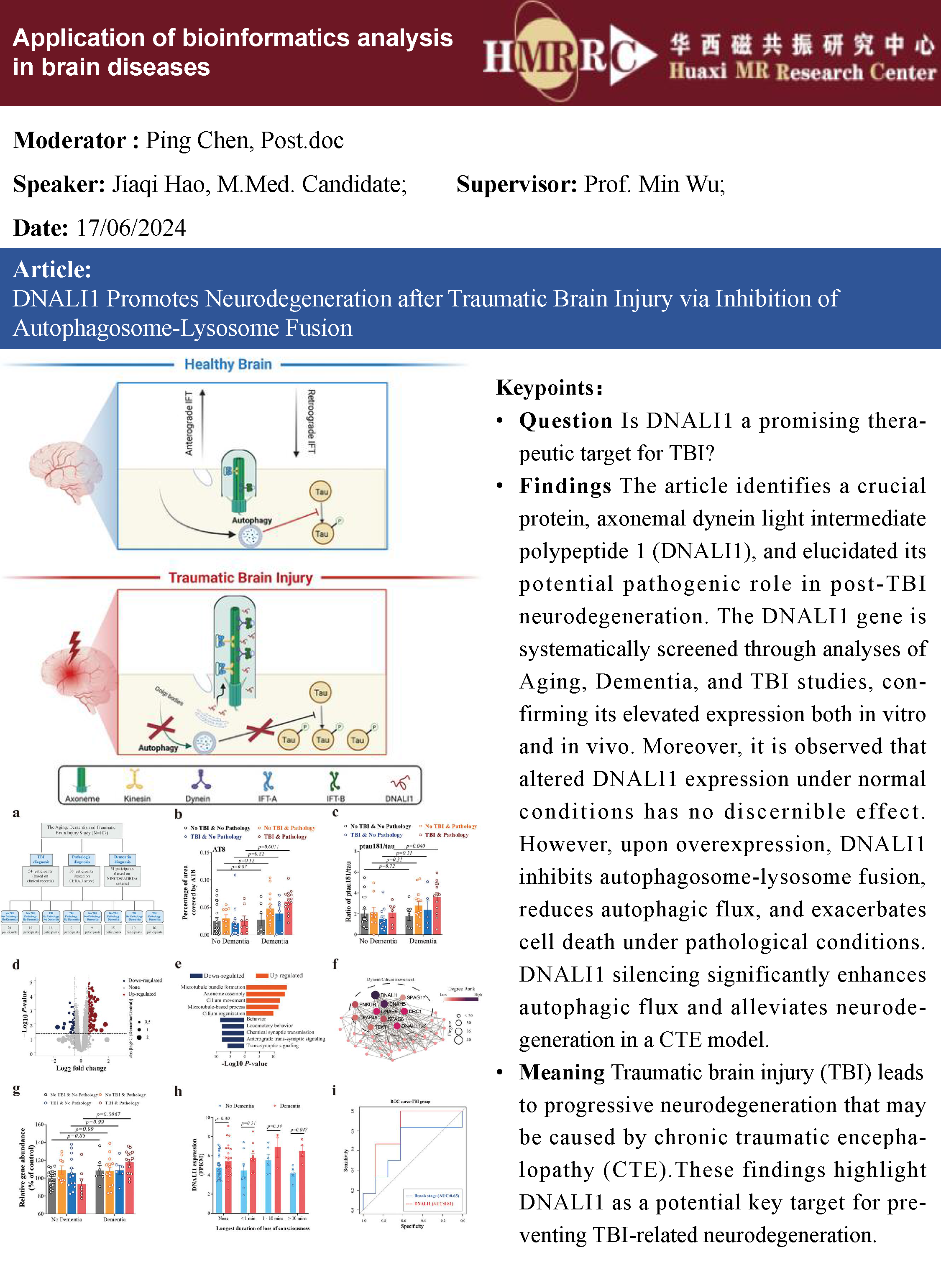
Question: Is ALOX15 a promising therapeutic target for GBM?
Findings: In this study, the researchers performed a genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screen in the presence of an iron death inducer (RSL3) and identified ALOX15 as a key driver of iron death. Angiopeptide-2-modified macrophage membranes were then used to encapsulate saALOX15-loaded mesoporous polydopamine to enhance the ability of the complex to cross the blood-brain barrier during targeted treatment of in situ GBM, producing a significant inhibitory effect on GBM progression and promoting radiosensitisation of GBMs.
Meaning: ALOX15 is a promising therapeutic target in GBM and proposes a biomimetic strategy dependent on MM biological properties to enhance the in vivo performance of NPs for the treatment of GBM.